Assay: 99% min
Appearance: White powder
Package: 25kg/bag
Sample: Available


Assay: 99% min
Appearance: White powder
Package: 25kg/bag
Sample: Available
Chemical Name: Sodium benzoate
CAS No.: 532-32-1
Molecular Fomula: C7H5NaO2
Chemical Structure: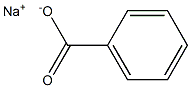
Molecular weight: 144.10317
Appearance: White powder
Assay: 99%min
Sodium benzoate Typical Properties
| Content % | 99.0 min | 99.25 |
| Loss on drying % | 2.0 | 1.5 |
| The Acid Alkalinity | ≤0.2ml | <0.2ml(on the principle of 0.1mol/l NaOH) |
| Colour of Solution | Y6 | Y6 |
| Chlorides % | ≤0.02 | ≤0.02 |
| Total Chlorine % | ≤0.03 | ≤0.03 |
| Heavy Metal(as Pb) | ≤0.001 | ≤0.001 |
| Arsenic % | ≤0.0003 | ≤0.0003 |
| Mercury % | ≤0.0001 | ≤0.0001 |
| Oxide | Meets the requirement | Meets the requirement |
1. Sodium benzoate, also known as sodium benzoate, is a food preservative commonly used in the food industry in China. It has an odorless or micro-scented benzoin odor and has a sweet taste. Stable in the air, it can absorb moisture in the exposed air. Naturally found in blueberries, apples, plums, cranberries, cranberries, prunes, cinnamon and cloves, its bactericidal properties are weaker than benzoic acid, and the bactericidal power of 1.180 g of sodium benzoate is equivalent to about 1 g of benzoic acid.
2. In an acidic environment, sodium benzoate has a significant inhibitory effect on various microorganisms. When the pH is 3.5, 0.05% solution can completely inhibit the growth of yeast, but when the pH is above 5.5, it has a poor effect on many molds and yeasts. There is almost no effect in an alkaline solution.
3. After sodium benzoate enters the human body, it combines with glycine to form uric acid or combines with glucuronic acid to form glucuronide during biotransformation, and all of it is excreted from the urine and does not accumulate in the body. It is a safer preservative in the normal dosage range and has no toxic effect on the human body. It can be used in carbonated drinks, concentrated juices, margarines, gum bases, jams, jellies, soy sauce, etc.
4. The daily allowable intake (ADI) is <5 mg/kg body weight (based on benzoic acid).
Sodium benzoate is more lipophilic, easily penetrates into the cell membrane, interferes with the permeability of the cell membrane, inhibits the absorption of amino acids by the cell membrane, enters the alkali storage in the ionized acidified cells of the cell, and inhibits the activity of the respiratory enzyme of the cell. The acetyl-CoA condensation reaction is prevented, thereby serving the purpose of food preservation.